Alopecia is a condition where hair loss occurs anywhere on the body, for a variety of different reasons. Male pattern baldness is a form of alopecia, for example. In this article, we will delve into the definition of alopecia, the different kinds of alopecia, some symptoms to look out for, and potential cures or treatments. Alopecia is a condition that Transitions Hair can help you work through. Drop us a line, and let us sit down, assess your hair health, and come up with a solution..
What is Alopecia?
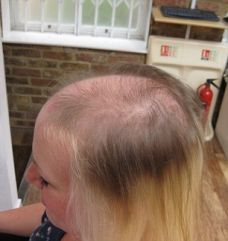
Alopecia means hair loss. There are different kinds of alopecia, from male or female pattern baldness, to where hair growth stops for a time before starting again.
There are various symptoms and different treatments. However, not all treatments work, and sometimes people are left to live with their hair loss. This condition can be tough on people, as we can define ourselves, and feel good about our hair.
Types of Alopecia
There are many forms of alopecia, with different symptoms and treatments.
Androgenetic Alopecia
This is male or female pattern baldness, often genetically passed down.
Men often present with a thinning or receding hairline. Women tend to present with diffuse thinning all over the head, while the hairline remains constant.

Alopecia Areata
This is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system suddenly attacks hair follicles anywhere on the body. It results in sudden hair loss, often on the scalp, but it can be anywhere. Typically hair loss happens in oval-shaped clumps.
Traction Alopecia
This type of hair loss is when hair is pulled too tightly, causing damage to the hair follicles. It is most commonly found in people who use hair ties, braids, or other types of hairstyle, which puts pressure on the hair follicles.
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
This is a rare condition affecting postmenopausal women. FFA causes progressive hair loss along the front hairline, temples, and eyebrows. It is usually accompanied by inflammation and scarring. It is an irreversible hair loss.
Alopecia Universalis
This is a rare form of hair loss that involves the complete loss of hair from the scalp and the entire body, including eyebrows, eyelashes, hair on the head, and elsewhere. It is believed to be a larger version of alopecia areata, where the immune system attacks all the hair follicles on a person’s body.
Alopecia Symptoms
Symptoms associated with alopecia include:
- Gradual thinning of the hair. This could indicate Androgenic alopecia in men and women. If you start to see this, Transitions Hair can help with male pattern baldness.
- Sudden loss of hair in small patches. This is a symptom of alopecia areata and should be checked immediately.
- Itching or burning where there is hair loss. This can be a symptom of alopecia areata and frontal fibrosing alopecia.
- Scarring and inflammation. This symptom is especially related to FFA and should be checked by a doctor.
- Broken hair. Hair that falls out easily or breaks easily can be a symptom of Traction alopecia.
- Total loss of hair from the scalp in a short space of time. This is a sign you may have alopecia universalis.
While all of the above are symptoms of alopecia, understand that hair loss can also be a result of other underlying conditions or a side effect of some medications. Always check with your doctor to understand the cause of your hair loss.

Causes of Alopecia
There can be many reasons one develops alopecia.
- Genetics. Pattern baldness is mainly handed down through the generations via genetics.
- Autoimmune disorder. Some forms of alopecia is the body mistakenly attacking hair follicles, causing hair loss.
- Medical conditions. Thyroid disorders, lupus, or even diabetes can contribute to alopecia.
- Trauma. Physical trauma to the skin, such as burns or scarring, can lead to hair loss.
- Stress. Being under considerable stress can lead to hair turning prematurely grey, or even the loss of hair.
- Nutritional deficiencies. A lack of iron or protein can lead to hair loss.
- Hormonal change. Changes in a woman’s hormones during pregnancy or menopause can lead to hair loss. Men can also have hormonal changes which can trigger alopecia.
Diagnosis of Alopecia
A dermatologist or your GP should make a diagnosis of alopecia. There should be a physical examination of the affected areas, plus a look at your medical history.
There can also be a pull test, where the medical professional tugs at a small amount of your hair to see how many strands come loose.
Some may do a scalp biopsy of the area of hair loss to determine the actual cause.
Treatment for Alopecia
There are some treatments for alopecia, both medical and natural. Transitions Hair has medical solutions to help women and to help men with alopecia.

Medical Treatments
Some of the medical treatments for alopecia are as follows:
- Topical medications. Topical medications applied to the scalp can help stimulate hair growth or slow down the rate of hair loss.
- Oral Medications. Medications can be prescribed for male and female pattern baldness.
- Steroid injections. These can be used to reduce inflammation and then stimulate hair growth in some auto-immune alopecia cases.
- Phototherapy. Using Low-Level laser light and LED light can be reduced, and hair growth can be stimulated.
- Immunotherapy. A chemical (cortisone) is applied to the scalp, triggering an allergic reaction. This can stimulate hair growth in cases of alopecia areata.
- Hair transplant surgery. This involves taking hair from part of the scalp that is not affected by alopecia and moving it to the scalp where hair has been lost.
Please note that not all cases of alopecia can be treated medically. Speak with the Transitions Hair, and with your GP to fully understand your treatment options.
Natural Treatments
There are some natural alternatives to try and help with hair regrowth or to help soothe the skin to stop hair loss.
Some of these natural remedies include the sulphur in onion juice promoting hair growth; increasing your iron intake, as low levels of iron have been linked to hair loss; or biotin, or vitamin B7, which you can get from eggs and mushrooms. B7 helps promote hair loss.
As always, speak with your medical professionals and the friendly team at Transitions Hair, for your best guide to alopecia treatments.
Prevention and Coping with Alopecia
It can be tricky preventing alopecia, especially if it is genetically inherited or you acquire an autoimmune disease.
However, eating a healthy diet with the nutrients mentioned above- Vitamin B7, iron, and sulphur, can help keep your hair healthy and strong.
Manage your stress levels to prevent hair loss.
Practice good hair care. Avoid overuse of hairstyles that pull and tug at your hair.
Coping with alopecia can be exceptionally challenging. It can be very emotional losing your hair, or having to cut your hair.
Transitions Hair understands this, and we can help you understand and cope with hair loss.
Seek support from friends and other people who have alopecia, and understand from those around you what it is and how you can live with it.
Experiment with wigs and hair pieces. Transitions Hair can help you with the best natural wigs in Sydney.
Embrace a new look. Sometimes you must embrace what is happening and style yourself to go with it. React positively and own it. It can be very empowering and educational for others with the same condition.
Free Hair Loss Consultation at Transition Hair
Alopecia can be an unsettling condition. Losing your hair and not knowing why can put you off your guard. There are reasons, however, and treatments. The team at Transistion Hair can help with treatments, wigs, and an understanding shoulder.
Contact us today for a free consultation. We want you to look and feel your best every day.